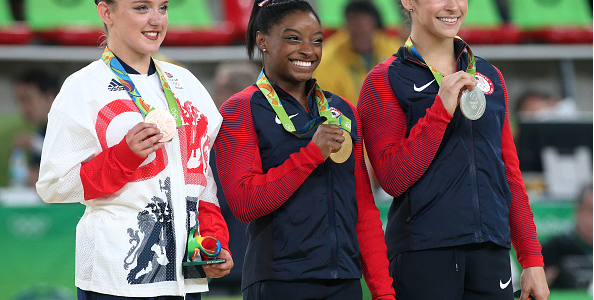Growing up in Southern California, I have watched over 12 Olympic Games and I’ve seen terrorism, political upheaval, defections, and amazing spirit. One thing I noticed in the behavior of the athletes is that the difference between earning a medal and not getting past the semi-final qualifications is attitude. At least “attitude” is what I called it before I went to grad school in Psychology. Now, I know it as “self-regulation”, or in lay-man’s terms, the ability to “deal.”
From the beginning of these 2016 Games in Rio, I watched the athletes deal with the highs and lows of the competition. As a psychologist, I think I enjoy the back stories more than the average person watching the games. The “up close and personal” pursuit of being the best and overcoming adversity is my passion in life. For the athletes, passion and dedication to the sport is a must, but it is most important to have the perfect trifecta of mind-body-spirit. When it comes to finally competing in the actual event, an athlete’s ability to regulate their fears, hopes, enthusiasm, confidence, and pain is the gold standard of winning.
Balance is a large part of the mind-body-spirit combination. An athlete needs to balance their breath and their heart beat even if they are scared to death. It would be so easy to stumble or over-arch when we don’t feel centered in our bodies.
My first example is of Katie Ledecky winning in the pool. 5 Medals. She was so excited at one point, she said it was the closest she felt to feeling like she would throw up while swimming. But, she didn’t. She won.
Michael Phelps needed to get into recovery before he could be such a great swimmer and win so many gold medals. He needed to, as they say, “check his ego at the door” and be a team mate. Learn to work well with others and be in his own zone, and not get distracted by his competitors.
Any time an Olympian shatters a world record by such a large margin, questions are inevitably raised. Hungary’s Katinka Hosszu swam the 400-meter individual medley with a world record by more than two seconds. Katinka has been drug tested 9 times in 2016 – most recently on June 21. “Confidence” was the drug that got her to win! Her coach/husband motivated her to be her best.
Take Simone Biles, her ability to balance her body and stick those landings is incredible. Said to be the best gymnast ever by Nadia Comaneci, Nadia herself was the athlete with the first perfect 10 in 1976. She says to USA TODAY, “I did what I used to do every day in the gym. It’s not like overnight I’d done something to surprise myself.” Bela and Marta were her coaches back then in Romania and they were the coaches of the US Women’s Gymnastics teams, helping them win decades of gold.
Márta and Bela Károlyi are Hungarian-Romanian gymnastics coaches and the national team coordinators for Team USA. After defecting to the US in 1981, they coached 9 world champions, sixteen European medalists and many U.S. national champions, including Mary Lou Retton and Kerri Strug. Marta focused on motivation and Bela focused on form.
Simone flies high with grace and takes to the ground like she has glue on her feet. Such precision, poise, and balance. She waivered on the balance beam itself, giving her a silver medal, but all others were gold. Did you know she also has a “mental strength coach”? You’ve probably seen Simone before her performances, placing her right hand on her stomach, closing her eyes, and taking a deep breath. In an interview with ESPN, her mental strength coach, Robert Andrews, said that relaxation techniques are exercises they’d been practicing in his office and he was pleased to see her using them to center herself before her events.
I can hardly think of other sports events where there is so much pressure. But, again, it is a very personal experience. Each sport has its challenges. Few have so many close “ties” by the hundredth of a second. Each athlete has their own story of redemption.
Mo Farah wins the 1000m, even after falling. How did he do it? Great attitude, planning out his strategy, kicking back until it was time to sprint to the front, and taking it. Usain Bolt is the “fastest man alive”, winning gold for 3 games in a row. He does it by using the energy of the crowd.
Many athletes pray before an event and give the glory to God. Their spirit is also calming and motivating. It seems to help a team when they pray together before they play together and against each other.
Visualizing your success is an extremely powerful way to get to the podium. Many of the athletes as children have written stories and drawn pictures of themselves winning in their sports of choice. They use those images, delaying gratification for years with discipline. Eventually grown up, being in the moment they visualized, revving themselves up while calming themselves down with positive affirmations.
There is a time and a place where the “agony of defeat” is expressed in a healthy way. Missy Franklin won gold in swimming in 2012 and this year she couldn’t keep up. She said she tried to stay as positive as possible. Her teammates say they love her spirit. She didn’t want to show her disappointment and bring her team down, so as she said, “she cried about it when she was alone” and to her mom.
It was extremely heart-breaking to watch the French runner Wilhem Belocian, after a split-second mistake took him away from his Olympic goals. After years of training, Belocian had only qualified for the 110m hurdles. Unfortunately, he was unable to contain himself and it caused him to bolt out of the starting blocks just a little too early. Electronically alarmed, the buzzer rang out and his hopes of a medal in Rio were over. You can jump the gun one time now and you are out. No “do-overs.” I felt for him. First in denial or shock, he held his head and then he became very angry, tearing off his official number and turning over hurdles. Eventually crying inconsolably, he gave in to the reality of his dashed dreams. You can’t blame him. Imagine all of the time, energy, and money leading up to the games. It is hoped he has a strong supportive network at home. He needs to be reminded that this same thing happened to Usain Bolt in 2011.
One thing that has always bothered me is how the quest for gold is so intense that getting a Silver or Bronze is “not good enough.” Getting qualified for the games and being an Olympian is great and every athlete could enjoy it to the fullest. But to win, you must have goals and there is nothing wrong with a goal of a gold medal.
There are so many examples of athletes using psychological self-regulation skills that I would be writing a 100 page dissertation.
And it has been scientifically proven. Studies at the University of Calgary, Canada, 2015, have found a correlation between self-regulation and world ranking. Athletes who are better at regulating their body’s response to stress–respiration rate, heart rate, and the activation of their muscles–are likely to perform better than those who struggle. Many elite athletes use biofeedback as part of their training. Then, they learn how to use their thoughts to control their physiological responses.
Self-regulation skills are a must in the games, and also a must in life. The competition of life is not as brutal most of the time, and sometimes the stakes are higher.
Learning self-regulation skills takes a good coach, a good trainer, a good therapist. In therapy, we call this flexing your “mental muscles” and it takes practice. It can ache like when you first go to the gym. Your therapist may give you exercises to help you focus and uncover who you are, which often feels worse before it feels better. Overall, life isn’t always “golden”, but you can get over hurdles by remembering the golden moments of life.
References
Dupee, M., Werthner, P., & Forneris, T. (2015) A Preliminary Study on the Relationship Between Athletes’ Ability to Self-Regulate and World Ranking. Biofeedback: Summer 2015, Vol. 43, No. 2, pp. 57-63.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M%C3%A1rta_K%C3%A1rolyi
http://www.nbcolympics.com/video/missy-franklin-trying-stay-positive-possible
_____________________________
Julie Olson, PhD, is a clinical psychologist in private practice in Orange County, CA. She has helped many people get over their challenges and find happiness. She can be reached at julieolsonphd@gmail.com.